What is the most common cause of cough in children?
The most common cause of cough in children is respiratory infections, particularly viral infections including:
- Common Cold (Viral Upper Respiratory Infection): Viruses such as rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, and coronaviruses are common causes.
- Influenza (Flu): Influenza viruses can cause more severe respiratory symptoms in children, including cough. The cough associated with the flu can be persistent and may last for several weeks.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV): RSV is a common virus that causes respiratory infections, especially in infants and young children.
- Croup: Croup is a viral infection that primarily affects young children, causing a distinctive barking cough.
- Bronchiolitis: This viral infection, often caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), affects the small airways in the lungs and can lead to coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
It’s important to note that while viruses are the primary cause of cough in children, other factors can contribute to persistent or severe cough, such as allergies, asthma, environmental irritants, or exposure to secondhand smoke. In some cases, bacterial infections like pneumonia can also lead to coughing in children. Treatment and management will depend on the underlying cause of the cough.
What are the 4 types of cough?
Coughs can be categorized into four main types based on their duration and characteristics:
- Acute cough: Less than three weeks and is often associated with viral upper respiratory tract infections, such as the common cold or flu.
- Subacute cough: Lasting between three and eight weeks, subacute coughs may be a continuation of an acute cough or the result of a lingering respiratory infection.
- Chronic cough: More than eight weeks in adults. Chronic coughs can be caused by various factors, including postnasal drip, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), asthma, or certain medications.
- Psychogenic or habit cough: This type of cough is not due to a physical condition but rather has a psychological origin. It may be triggered by stress, anxiety, or habit and can sometimes be challenging to diagnose and treat.

What is bronchitis cough and what does it sound like?
Bronchitis cough in children is often a result of inflammation in the air passages that lead to the lungs. Acute bronchitis, commonly triggered by viral infections like the flu or cold, can bring about this persistent cough. The cough associated with bronchitis can linger even after other symptoms have improved, making it a concern for parents.
A bronchitis cough can have distinctive sounds often described as:
- Productive Cough or a Wet and Phlegmy Sound
- Rattling or Gurgling from significant buildup of mucus in the airways
- Wheezing or a high-pitched whistling sound that can occur during both inhalation and exhalation
- Persistent and Hacking, lasting for several weeks
What is pneumonia cough like?
Keep in mind that individual experiences can differ, and not everyone with pneumonia will necessarily exhibit the same symptoms. Here’s a description of what a pneumonia cough may be like:
- Wet or Productive Cough
- Persistent and Intense, more so than a typical cough
- Chest Pain from the act of coughing
- Shortness of Breath
- Wheezing or Crackling Sounds
It’s crucial to note that pneumonia symptoms can overlap with other respiratory conditions, and a healthcare professional is best equipped to diagnose and determine the appropriate treatment.
What is an asthma cough like?
Asthma coughs can have specific features that distinguish them from other types of coughs like the following:
- Dry and Hacking, may not produce much phlegm
- Wheezing during both inhalation and exhalation.
- Cough Triggers like allergens, irritants, exercise, or respiratory infections
- Cough Variability in intensity and frequency, depending on triggers
- Night-time Cough and sleep disturbances
- Shortness of Breath
It’s important to recognize that asthma symptoms can vary among individuals, and not everyone with asthma will experience the same cough characteristics. If someone is suspected of having asthma, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.

What does a RSV cough sound like?
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that can cause respiratory infections, especially in young children. The cough associated with RSV infection can have distinct features like:
- Severe Coughing Spells, rapid and forceful
- Wheezing is common in RSV infections
- Rapid Breathing during coughing episodes
- Noisy or Rattling Breathing
- Difficulty in Breathing, such as flaring nostrils, chest retractions and faster breathing
It’s important to note that RSV infections can range from mild to severe, and some individuals, especially infants and young children, may develop more severe symptoms requiring medical attention.
What does Croup cough sound like?
Croup is a respiratory condition that primarily affects young children, causing inflammation of the upper airways, particularly the larynx and trachea. Here are some key features of a croup cough:
- Barking Cough like a barking seal or a honking noise
- Stridor, a high-pitched, musical or wheezing sound heard during inhalation
- Hoarseness
- Symptoms Worse at Night, may be more pronounced during sleep
- Resonance in the Chest
It’s important to note that croup symptoms can vary in severity, and not all children will exhibit the same degree of coughing or stridor. Croup is commonly caused by viral infections, with parainfluenza virus being a common culprit. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly if croup is suspected.
How can I stop my child from coughing?
If your child is experiencing a cough, there are several home remedies and general measures you can try to help alleviate their symptoms. However, it’s important to note that if your child’s cough persists, worsens, or is associated with other concerning symptoms, it is crucial to seek advice from a healthcare professional. Here are some general tips below to help stop your child from coughing.
What are some home remedies for cough in a child?
- Maintain Hydration with water, clear soups, or diluted fruit juices
- Use a Humidifier because adding moisture to the air can help ease coughing, especially if the cough is due to dry air
- Provide Honey (for children over 1 year old) for its natural soothing properties by mixing a teaspoon of honey with warm water
- Elevate the Head of the Bed or use a thicker pillow
- Encourage Rest
- Use Saline Nasal Drops to alleviate nasal congestion
- Avoid Irritants like tobacco smoke and strong odors
- Over-the-Counter Cough Medications (if appropriate): Depending on your child’s age and the specific cough symptoms, some over-the-counter cough medications may be suitable. However, always consult with a healthcare professional before giving any medications to a child.
Remember that these suggestions are general and may not be suitable for all situations. If your child’s cough persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, seek advice from a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

What is the fastest way to cure a cough for kids?
It’s important to note that there is no guaranteed “fast” cure for a cough, and treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the cough. Many coughs in children are caused by viral infections, and these typically resolve on their own over time. However, you can try the measures mentioned above, which may help alleviate symptoms and promote a faster recovery.
If your child’s cough persists, worsens, or is associated with other concerning symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and guidance on appropriate treatment. Additionally, if cough and cold medications are needed to alleviate cough in young children, also seek help with a doctor.
What to do when a child coughs at night?
When your child first starts coughing, try out some home remedies suggested below, which can provide some relief. However, if the nighttime cough persists, it’s crucial to consult a doctor, as it could be indicative of a worsening respiratory infection, bronchitis, asthma, or postnasal drip.
How can I stop my child from coughing at night naturally?
Coughing at night can be distressing for both children and parents. Here are some strategies to help manage a child’s nighttime cough:
- Use a Humidifier
- Elevate the Head of the Bed or use a thicker pillow to help with postnasal drip
- Stay Hydrated
- Create a Comfortable Sleeping Environment like a cool, dark room and establish a calming bedtime routine
- Nasal Saline Drops
- Encourage Steam like from a warm bath which can help soothe the airways
Otherwise, if the nocturnal cough is not resolving with some of these home remedies:
- Over-the-Counter Cough Medications (if appropriate) depending on your child’s age
- Consult a Healthcare Professional if your child’s cough persists, worsens, or is associated with other concerning symptoms
What are the signs of asthma in a child?
Asthma in children can manifest in various ways, and the signs and symptoms may vary from one child to another. Common signs of asthma in a child include:
- Frequent or Recurrent Coughing, especially at night or during physical activity
- Wheezing is often heard during exhalation
- Shortness of Breath
- Chest Tightness
- Frequent Respiratory Infections
- Coughing or Wheezing After Exposure to allergens (such as pollen or pet dander), irritants (such as tobacco smoke or strong odors), cold air, or exercise
- Night-time Symptoms, sleep disruption and fatigue
It’s important for parents to be vigilant for these signs and to seek medical attention if they suspect their child may have asthma. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for controlling asthma symptoms and improving the child’s quality of life.

When should I be concerned about my child’s cough?
While most coughs in children are caused by common respiratory infections and are not typically a cause for major concern, there are certain signs and symptoms that may indicate a more serious issue. You should seek prompt medical attention if:
- Persistent or Recurrent Cough more than a couple of weeks
- Difficulty Breathing
- Wheezing
- High or Persistent Fever
- Coughing Fits or Violent Coughing
- Blue Lips or Face from a lack of oxygen
- Associated Symptoms such as lethargy, dehydration, persistent vomiting, or refusal to eat or drink
- Underlying Health Conditions like asthma or a compromised immune system
Trust your parental instincts. If you are concerned about your child’s cough or overall well-being, it is always appropriate to seek advice from a healthcare professional.
Will a child’s cough go away on its own?
In many cases, a child’s cough will resolve on its own, especially if it is caused by a viral respiratory infection, which is a common scenario. Coughing is the body’s natural response to clear the airways of irritants and mucus.
However, the duration of a child’s cough can vary based on factors such as the underlying cause, the child’s overall health, and the presence of any other medical conditions.
Coughs caused by viral infections, such as the common cold, typically last for a week or two but can linger for a bit longer in some cases. If the cough persists, worsens, or is associated with difficulty breathing, high fever, persistent vomiting, or other worrisome symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
How long should a cough last in a child?
The duration of a cough in a child can vary based on the underlying cause, and it’s not uncommon for the duration to differ from one child to another. In general, the duration of a cough in children is often influenced by the cause of the cough:
- Viral Respiratory Infections (Common Cold): Coughs caused by common viral infections, such as the common cold, typically last for about 1 to 3 weeks.
- Croup: Croup coughs often peak around the third to fifth day of illness and may last for several days.
- Bronchiolitis: In infants, bronchiolitis, commonly caused by RSV, can lead to a persistent cough. The cough may last for several weeks, and the severity can vary.
- Asthma: Asthma-related coughs may be intermittent or chronic, and the child may experience episodes triggered by various factors.
- Pertussis (Whooping Cough): Pertussis is a bacterial infection that can cause prolonged coughing fits. The coughing spells may last for several weeks, and the condition often requires medical attention.
It’s important to note that if a child’s cough persists for an extended period, is associated with difficulty breathing, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional.

Can a child’s cough be serious and when is a cough serious?
Yes, a child’s cough can be serious, depending on the underlying cause. While many childhood coughs are caused by common viral respiratory infections and are not typically serious, here are situations where a cough may indicate a more significant or potentially serious health issue:
- Difficulty Breathing
- Persistent Cough especially beyond 3 weeks
- Wheezing
- Coughing Fits or Violent Coughing, may be a sign of conditions like croup or pertussis
- Blue Lips or Face
- Associated Symptoms like lethargy, dehydration, persistent vomiting, or refusal to eat or drink
It’s crucial for parents to trust their instincts and seek medical attention if they are concerned about their child’s cough. Early identification and management of serious respiratory issues are essential for the well-being of the child.
What causes prolonged cough in children?
A prolonged cough in children, lasting for several weeks or more, can be attributed to various underlying causes, including:
- Asthma, especially if the condition is not well-managed
- Allergies to environmental allergens (pollen, dust mites, or pet dander)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Postnasal Drip or Excessive mucus dripping down the back of the throat
- Respiratory Infections like pertussis (whooping cough)
- Environmental Irritants like tobacco smoke or air pollution
If a child has a prolonged cough, especially if it is associated with other concerning symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional.
How do I know if my child’s cough is viral or bacterial?
Distinguishing between a viral and bacterial cough based solely on symptoms can be challenging, as both types of infections can have overlapping characteristics. There are occasionally certain general patterns that may differentiate.
Viral coughs can have a gradual onset, associated with runny or stuffy nose and low grade fever. It can affect multiple systems, leading to symptoms like bodyaches, fatigue and sometimes gastrointestinal symptoms.
Bacterial coughs can have a more sudden onset presentation, associated with high fever or persistent fever, a more productive cough and localized symptoms like chest pain and difficulty breathing.
It’s important to note that these generalizations may not apply to every case, and the distinction between viral and bacterial infections is not always straightforward. Oftentimes, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional, as they can conduct a thorough evaluation.

Does a viral cough need antibiotics?
No, a viral cough does not typically require antibiotics. Antibiotics are effective against bacterial infections, not viral infections. Most common respiratory infections, such as the common cold, influenza (flu), and many cases of bronchitis, are caused by viruses. Antibiotics have no impact on viruses and, therefore, are not useful in treating viral infections.
Using antibiotics inappropriately, such as for viral infections, can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve and become resistant to the effects of antibiotics, making the drugs less effective in treating bacterial infections.
For a viral cough, the focus of treatment is on managing symptoms and allowing the body to naturally overcome the infection. Supportive measures include rest, hydration and sometimes over-the-counter medications.
Does my child have a chest infection?
This can be difficult to determine just based on a child’s symptoms. Some symptoms of a chest infection may include:
- Persistent Coughing with phlegm
- Chest Pain particularly during coughing or breathing deeply
- Shortness of Breath
- Fever
- Wheezing
- Difficulty Sleeping and Fatigue
If your child is experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can conduct a thorough examination, take a medical history, and may recommend additional tests, such as chest X-rays or laboratory tests, to determine the cause of the symptoms.
When do you need antibiotics for a cough?
Antibiotics are effective against bacterial infections, but they are not effective against viral infections, which are a common cause of coughs. Therefore, antibiotics are typically not prescribed for viral coughs, such as those associated with the common cold or influenza.
In general, antibiotics may be considered for a cough when the underlying cause is determined to be a bacterial infection. Some situations in which antibiotics might be prescribed for a cough include:
- Bacterial Respiratory Infections like bacterial pneumonia
- Strep Throat is also caused by bacteria
It’s important to note that many respiratory infections, especially those caused by viruses, do not require antibiotics. Using antibiotics inappropriately, such as for viral infections, can contribute to antibiotic resistance, where bacteria become resistant to the effects of antibiotics.
If you or your child has a persistent or severe cough, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. If a bacterial infection is suspected, they may prescribe antibiotics. However, it’s crucial to follow the healthcare provider’s advice and complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This helps prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
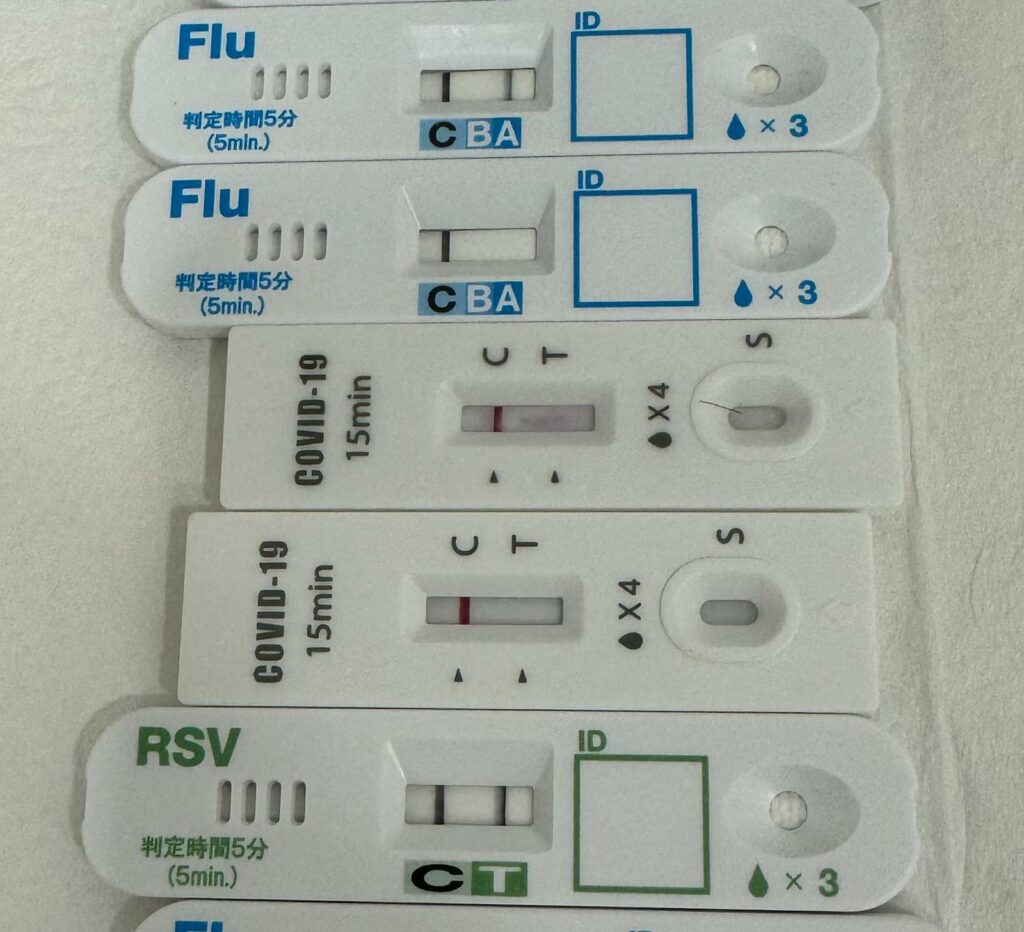
Paddington Medical offers viral testing for Influenza, Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Adenovirus, COVID and many others. We do viral testing to get an accurate diagnosis of you, or your child’s medical condition so as to advise you appropriately. Furthermore, if the pathogen is RSV, Influenza or Adenovirus, you do not need antibiotics to treat these, and hence we can reduce the misuse or inappropriate prescription of antibiotics!
Check out this article on “My child has a high fever, runny nose, blocked nose and cough, what do I do now?” where we talk about rapid testing for common viruses in children.
GET IN TOUCH
Schedule a Visit

Dr Lee Joon Loong
Medical Director
MBBS (Australia)
Graduate Diploma in Geriatric Medicine
Designated Workplace Doctor (CAW)
EIMS Primary Care Physician
Certificate Course in Andrology (Men’s Health)
Dr Lee is in Clinic on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Friday, Saturday.
Dr Lee’s surgical procedure days are on Tuesday and Thursday